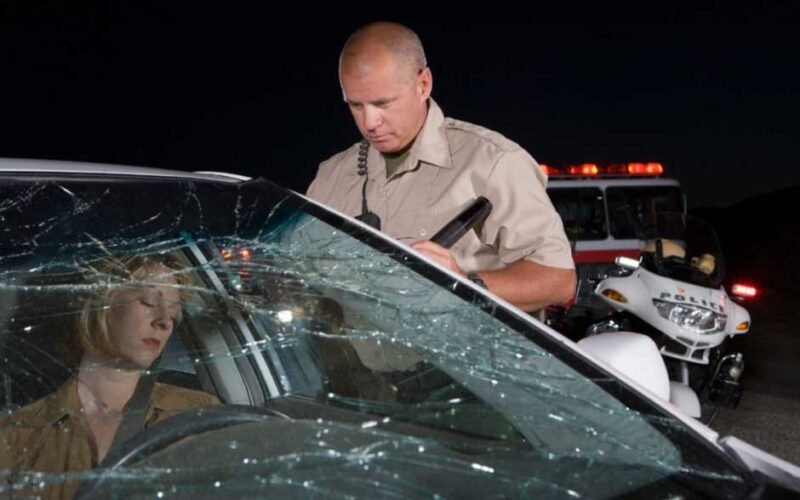
Car accidents rarely have simple causes, and determining who is legally responsible can be just as complicated. After a crash, those involved often face injuries, property damage, and emotional stress. The question of liability is who pays for what matters, not just for insurance claims but also for any legal action that might follow.
Knowing which parties could be held liable is key to getting fair compensation and moving forward. When looking at liability, it is crucial to recognize that more than one party can be responsible for an accident.
The law considers various factors, such as driver behavior, vehicle ownership, employment relationships, and even product defects. This is why it is best to get help filing a claim after a car accident.
Here are the parties that can be liable for a car accident:
Drivers
Most often, the driver whose actions directly caused the accident is held liable. Negligence, like running a red light, speeding, distracted driving, or driving under the influence, is familiar ground for assigning fault.
A police report, witness testimony, and traffic camera footage often play a central role in establishing what happened and who is responsible.
Vehicle Owners
Sometimes, the person driving is not the owner of the car. If the owner allowed someone unfit, such as an unlicensed or intoxicated person, to use their vehicle, the owner may share liability for any resulting accident. This is especially relevant if the owner knew about the risks but handed over the keys anyway.
Employers
If the driver was working at the time of the crash, their employer might be liable under the legal concept of vicarious liability. This applies when someone causes an accident while performing job duties, such as a delivery driver or a company employee running errands for work. In these cases, both the driver and the employer could be responsible for damages.
Manufacturers
Not all accidents are caused by human error. Sometimes, a vehicle defect such as faulty brakes or airbags contributes to a crash. Under product liability rules, a defective part may be held accountable for any accidents it causes.
This type of claim requires proving that the defect existed and directly caused the accident or injuries.
Other Potentially Liable Parties
Liability can sometimes extend to parties other than drivers, owners, and manufacturers. For example, government agencies might be responsible if poor road conditions or inadequate signage contributed to the accident.
In rare cases, passengers, pedestrians, or cyclists could also share some responsibility, depending on their actions before the accident.
Shared Liability
It is common for more than one party to be at fault. Many states use comparative negligence rules, which means each party is assigned a percentage of fault. Compensation is then adjusted based on each party’s share of responsibility.
In no-fault states, each person’s insurance covers their losses, but there are exceptions for severe injuries.
Wrap Up
Car accident liability is not always clear-cut. Drivers, vehicle owners, employers, manufacturers, and sometimes even government agencies can all contribute to a crash. The specific facts of each case determine who is responsible and to what extent.
Knowing these possibilities helps anyone involved in a car accident take the proper steps toward fair compensation and resolution.